- By Vanshika Choudhary
- July 1, 2025
In today’s very quickly changing supply chain landscape, the demand for smarter, more agile, highly automated warehouses has never been higher. The diurnal rises of RFID with IoT and AI in the realm of warehouse automation are leveling up the entire concept. This integration is working together to streamline operations and create efficiencies, as well as provide accuracy and scalability not possible previously. This blog focuses on exploring the interaction of technologies, their transformative power for warehouse automation, and the future possibilities.
Warehouse Automation Undergoing A Transformation
From the days of simple conveyor belts and manual inventory checks, warehouse automation has come a long way. Today, modern automation entails a plethora of technologies purposed to reduce and even eliminate human intervention in functions such as receiving, picking, packing, and shipping, with a view to making warehouses faster, more accurate, and more economical throughout the life of the warehouse.
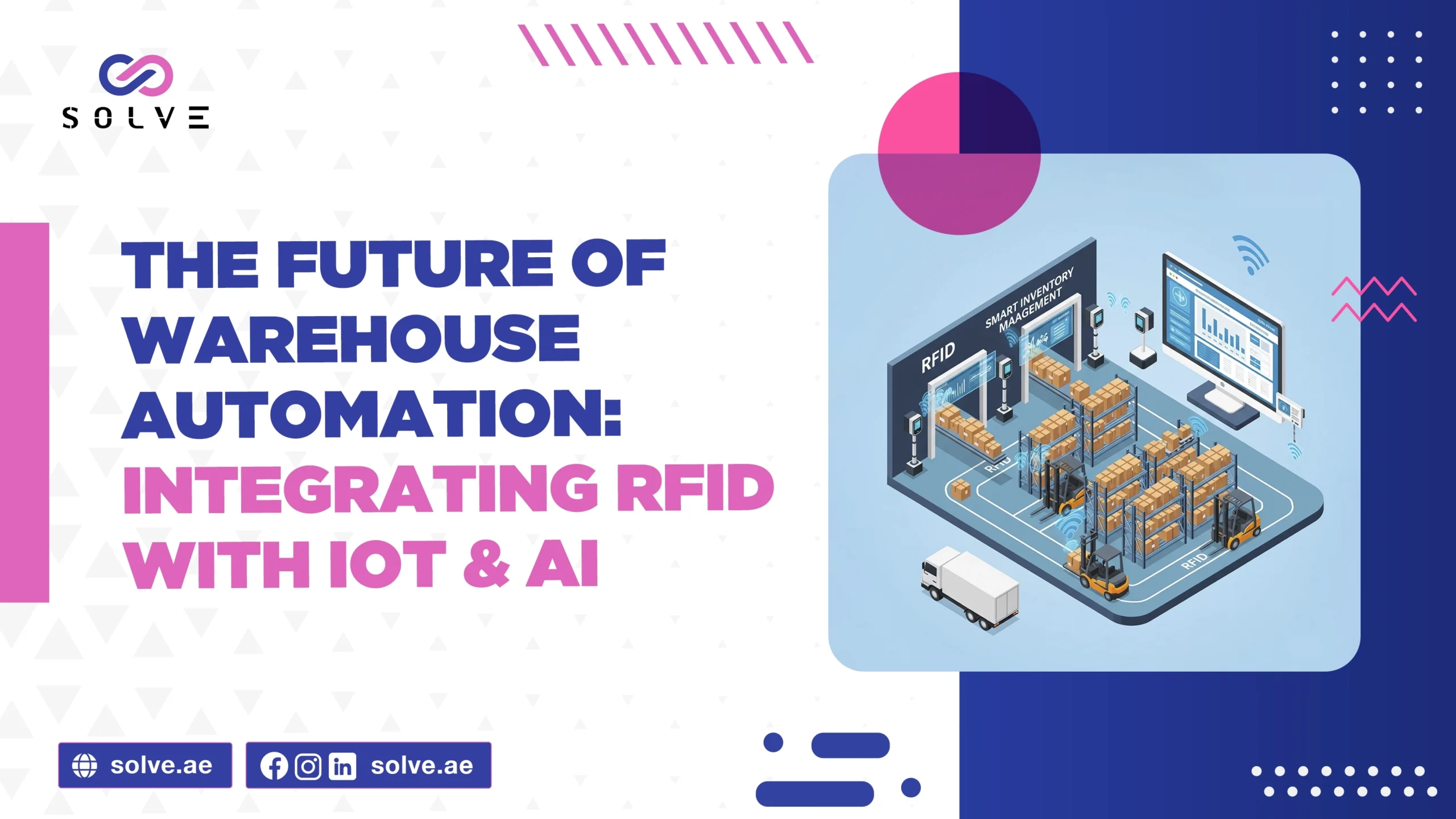
RFID forms the spine of a modern warehouse automation system.
Using radio waves, RFID systems can locate and identify objects automatically, hence providing the finishing touch to any modern warehouse procedure. Barcode systems need their scanners to see the bars, but RFID tags use and scan from afar, thus speeding up the inventory process and making it more accurate.
Automated Tracking and Real-Time Data: Attach RFID tags to a product or pallet, allowing them to be scanned automatically as they move through the warehouse. When items arrive, RFID readers record them into the system instantaneously, thus bypassing manual data entry and limiting errors.
Mass reading and efficiency: This reading methodology allows the reading of thousands of tags at one time, greatly reducing the time spent on counting inventory. Besides saving time, this efficiency lowers labor costs and reduces human error. Check out opur latest blog post on Top Drawbacks of RFID in Warehouse Management
Improved Customer Experience: RFID helps warehouses to provide accurate deliveries on time by way of better stock tracking mechanisms that limit stockouts and overstocks. And in return, reliability breeds customer satisfaction, plus about the goodwill for the company.
IoT: Building the Connected Warehouse
The Internet of Things is a web of interconnected devices like sensors, beacons, and smart equipment working to receive and share data inside the warehouse environment. Together with RFID with IoT and AI acts as the backbone to build a fully connected and smart ecosystem within the warehouse.
Environmental Monitoring with Smart Sensors:
The IoT sensors keep monitoring the temperature, humidity, and air quality at the warehouse site. These checks are especially done for perishables and sensitive goods should an event occur where managers would be immediately alerted if an environment parameter was out of an allowable safe limit.
Real-time Asset and Inventory Tracking:
Using RFID tags and beacons, IoT allows these goods and gadgets to send out precise location information in real time. This tracking mechanism follows any item of interest right now; this helps reduce the time spent tracking misplaced stock. This visibility then facilitates optimum utilization of space and productive work planning.
Centralized Data Management:
Also, all the data transmitted by an IoT device or an RFID reader, etc., is aggregated in the cloud, presenting a unifying dashboard at the disposal of warehouse managers. This approach centralizes monitoring so that they may observe warehouses remotely, come to decisions swiftly, and even integrate this into any other business system.
AI: Turning Data into Actionable Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is the life force that turns those rivers of data coming in from RFID and IoT into actionable insight. In a very literal sense, the application of machine learning and advanced analytics is what drives the continuous improvement of warehouse operations.
Demand and Inventory Predictive Analytics:
Moreover, using AI algorithms based on historical and real-time data, demand trends can be forecasted, and stock levels can be optimized. This predictive ability ensures that warehouses can forecast customers’ needs, avoid stockouts, and reduce inventory holding, thereby cutting costs and enhancing service levels.
Anomaly Detection and Quality Control:
Machine learning models keep track of inventories moving in and out, as well as equipment usage, to detect any anomalies or irregular patterns. In one instance, if some batch is frequently misplaced or if some machine is not working along prescribed parameters, the AI informs of these anomalies for immediate attention so that the errors are not allowed to propagate further.
Continuous Learning and Process Improvement:
Additionally, AI systems learn about every transaction and operational occurrence and work to improve their algorithms accordingly. With this, not only will the warehouse become smarter and more efficient, but it will also be able to keep up with the changing business needs and market conditions.
Conclusion
The integration of RFID with IoT and AI stands as the prime mover for the change in warehouse automation. By way of automation in tracking and providing real-time visibility and actionable intelligence to data, these technologies establish new parameters on efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability. Contact us as the acceptance levels continue to rise; such warehouses investing in digital changes will have a much better chance of staying viable in an increasingly aggressive, fast-paced, global market. The future of warehouse automation doesn’t stand for just machines anymore—it’s in creating nurturing smarts and reactive, safe supply chains for tomorrow.