- By Vanshika Choudhary
- March 13, 2025
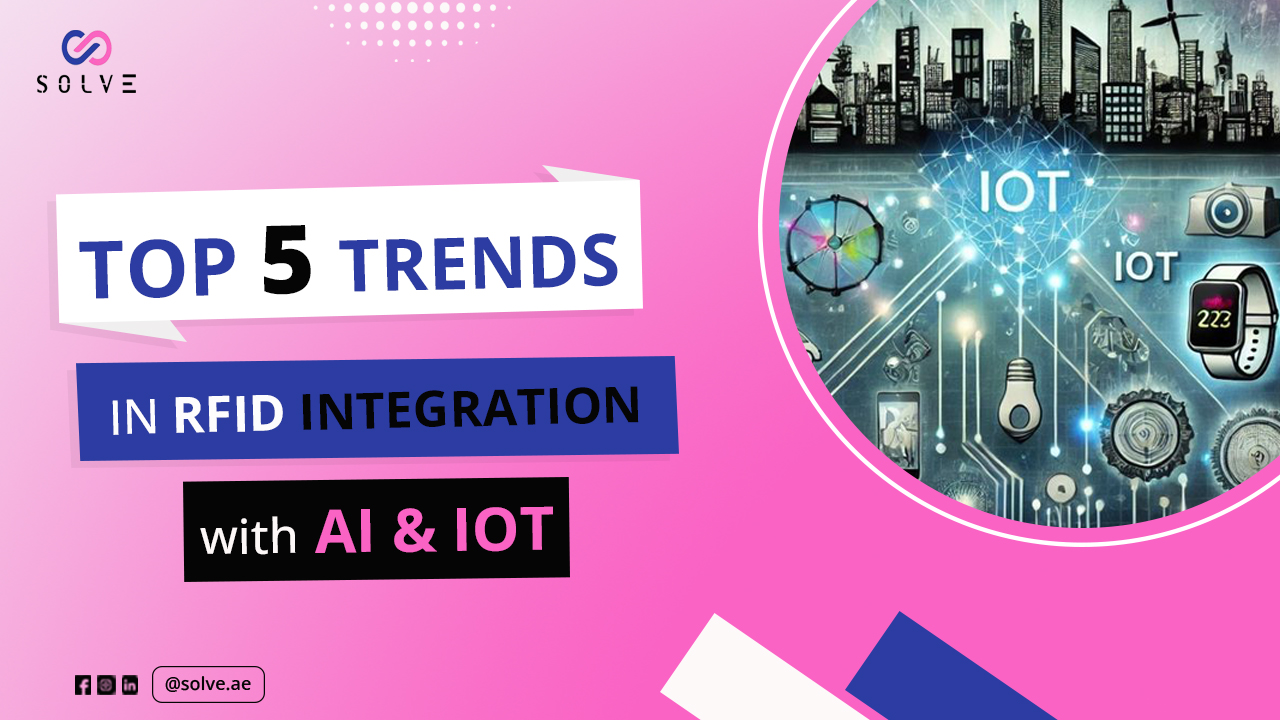
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), when combined with AI (Artificial Intelligence) and IoT (Internet of Things), is changing the landscape of industries around the world, creating efficiencies, cutting costs, and taking off a load from decision making. The blog encompasses the top trends that are witnessing RFID diversification with AI and IoT, including applications, benefits, and future visions.
RFID technology has existed for many years and has mainly been used to track or identify objects. However, when paired with AI and IoT, fans have opened new avenues. AI augments the RFID system with real-time insights and predictive analytics, while IoT connects the RFID devices to a wider network of sensors and devices for real-time monitoring and control.
The Value of Integration
The integration of RFID with AI and IoT allows sophisticated data analysis and automation. Within supply chains, RFID tags track inventories in real time, while AI processes this information to predict stock levels and optimize logistics. IoT enables this information to be accessible through different platforms and devices.
Objective
This blog will elaborate on the trends emanating from RFID integration with AI and IoT in terms of applications and benefits to their transformations to the businesses in the various industries. It will provide businesses with knowledge on how they can take advantage of these technologies to improve operations and consequently remain competitive.
Trend 1: Universality across Industries
Examples of Applications in Healthcare
Patient tracking, asset management, and administration of prescriptions are uses of RFID in the healthcare sector. For example, RFID wristbands are used to control the movements of patients to ensure that they receive the right treatment at the right time. This provides not only better patient safety but also manages the operations of hospitals efficiently.
Innovations in the Educational Sector
Tracking attendance, management of library books, and monitoring equipment are all possible applications of RFID in education. This helps to lessen administrative duties and improve the distribution of resources. For example, an RFID-enabled library system will automatically check out books as they are removed from the shelf.
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
RFID is important in logistics for tracking and managing inventories. RFID makes it possible for companies to know where their goods are in real-time and hence reduce theft and loss. AI can also analyze this information, check routes, and predict delivery times, which improves customer satisfaction.
Trend 2: Integration into the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Intelligent Supply Chains
In this sense, RFID and IoT integration would create a modern smart supply chain. The raw materials, semi-finished products, and finished products are all connected. It would enable real-time monitoring of inventory levels, shipment locations, or conditions of individual products. IoT sensors would detect, for example, temperature changes, humidity levels, or vibrations to ensure safe storage and transportation of products.
Managerial Supervision Automated Inventory
The management of an automated inventory uses RFID distributed systems connected with the IoT, which continually send stock readings and external alerts on when things are to be bought back into inventory. Therefore, there is a reduction of human error as collections are at perfect product levels. AI may also use inventory data to predict consumption-demand trends and optimize stock levels.
Real-Time Monitor Decisions
IoT allows for RFID data to be accessed by different platforms and devices, making possible real-time decision making. Managers can monitor operations remotely and then respond quickly to problems such as stock-outs or delays. That kind of flexibility is essential in fast-moving industries such as retail and manufacturing.
Trend 3: Artificial Intelligence (AI) Improvements
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics are involved in the augmentation of the RFID systems through the virtue of AI. For instance, in a retail setting, the application of AI will analyze the inventory-level information obtained from RFID concerning customers within the store and then predict sales trends for optimizing stock levels. This makes sure that the stores are stocked up with the right products at the right time.
Personalized Experience for Customers
AI and RFID can work together to provide personalized experiences for customers in retail. It can, for instance, analyze RFID data across purchased items and preference behavior to target households with promos and recommendations, ultimately enriching customer engagement and loyalty. check out our latest blog post on Understanding your website development Budget: what to expect and how to plan.
Specific Pricing and Optimization of Stocks
AI makes dynamic pricing possible through analyzing RFID data. It keeps tabs on stock levels and demand for a real-time view, enabling price adjustments to maximize profits. It further optimizes stock levels in accordance with sales forecasts to eliminate too much waste or additional excess stock.
Trend 4: Intelligent Tags and Environmental Sensors
Entering smart tags
Smart RFID tags are equipped with processing power and can do more than identification tasks. They can as well store data, perform calculations, and go as far as communicating with other devices. This makes such tags very suitable for real-time data processing applications.
Environmental Sensors
RFID tags that have their own environmental sensors monitor temperature, humidity, and so on, and those that make sense in industries such as food logistics and pharmaceuticals, where products must be placed into certain environments to remain quality and safe.
Application Within Food Logistics
For instance, a smart RFID tag can monitor the temperature around perishables during transport in food logistics. If the temperature exceeds the limits considered safe, it alerts the logistics managers to act fast to prevent spoilage. This reduces waste and delivers safe products to consumers.
Benefits for Pharmaceuticals
For the pharmaceutical industry, an RFID with a sensor type can monitor the storage environment for sensitive medicines. This leads to increased compliance with regulatory requirements, hence upholding the efficacy of the drugs. Also, it can trace authenticity to compete against counterfeiting.
Trend 5: The Incorporation of Emerging Technologies
Integrating Blockchain
RFID could be used with its counterpart, blockchain, in the ensuring of a secure and transparent supply chain. Blockchain technology has the potential to ensure that data collected from RFID is not tampered with while also making it accessible upon demand by all stakeholders. This particular characteristic will definitely enhance confidence and accountability. Such instances would be particularly worthwhile in industries in which authenticity and sources of the said products matter.
Track Application under Secure Supply Chain Environments
RFID-blockchain technology can be ushered into secure supply chains by tracking every movement of a product, from raw materials to the end consumers. Thus, RFID proves that products are original and have not been tampered with during the journey from a maker to a consumer. It also helps to track sources of products, which is a very important segment in complying with packaged checks and balances, especially for food items.
The advancement in RFID will continue to give rise to emerging possibilities with respect to the developments of blockchain and edge computing with time. As maturity is gained by these developing technologies, a great deal of sophistication in applications will be brought about that will even ensure that security, efficiency, and transparency extend to industries all around.
Conclusion
As seen above, using RFID in terms of artificial intelligence and IoT is indeed changing the industry because it becomes very efficient, provides much better decisions, and improves cost savings. Contact us as Some transformations are driving this new transformation towards RFID, such as widespread adoption, IoT integration, enhanced AI, smart tags, and integration with new emergent technologies.