- By Vanshika Choudhary
- April 9, 2025
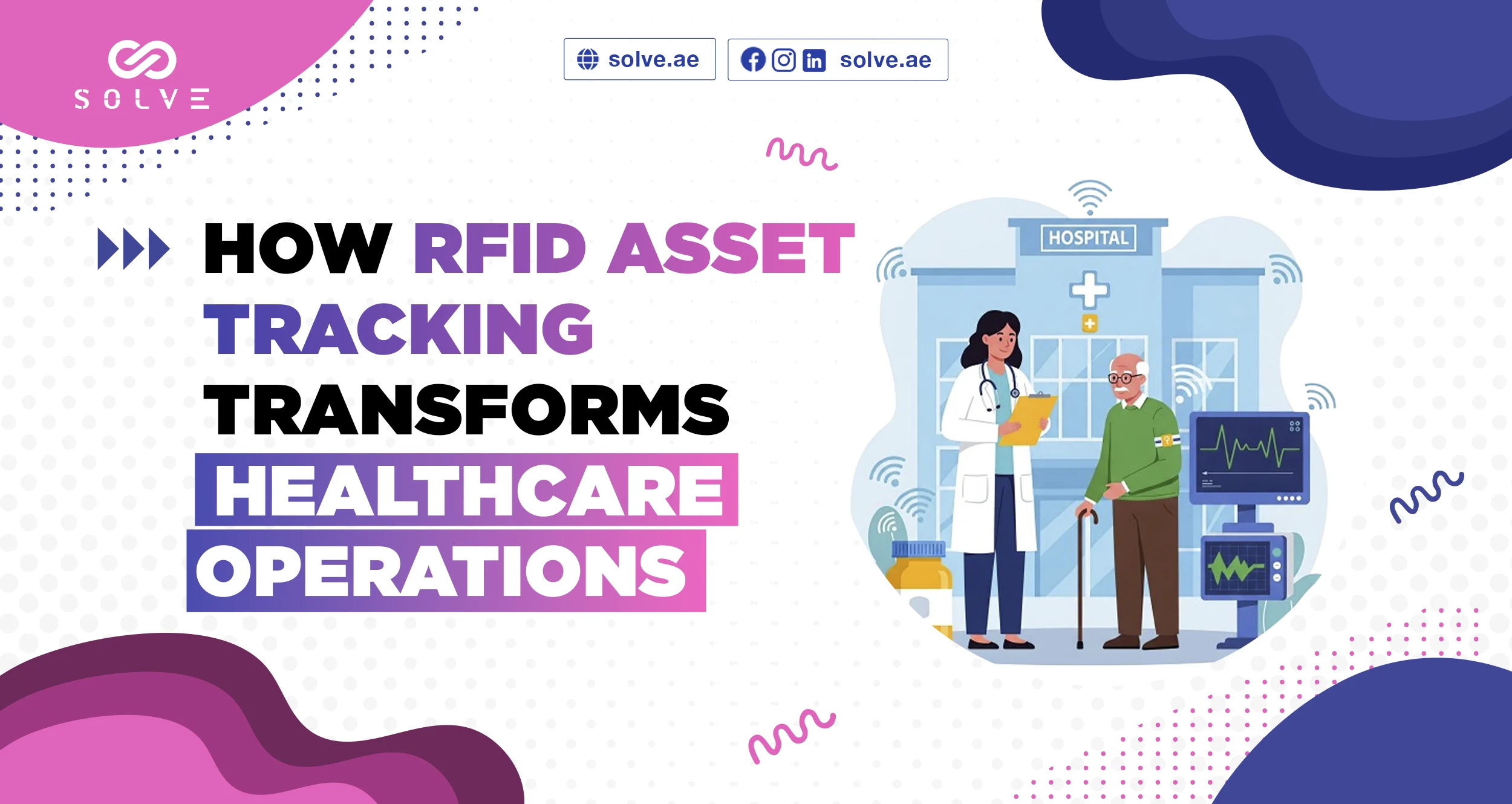
RFID technology, or Radio Frequency Identification is transforming healthcare processes with more efficiency, improving patient care, and cutting costs. RFID systems have become indispensable and have been introduced as a new tool in modern-day healthcare facilities to track medical equipment, supply items, and even patients in real time. This blog elaborates on how RFID asset tracking is impacting the entire healthcare operations, applications, benefits, and the challenges faced.
Understanding RFID Technology
RFID technology identifies electronically readable information and tracks it through electromagnetic fields by attaching this information to various objects. In healthcare, RFID technology is utilized for tracking medical assets, inventory management, patient movement tracking, and compliance with safety protocols. The operation of the technology is done through different electromagnetic frequencies, such as low-frequency (LF), high-frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF), where each frequency finds its application based on range and interference tolerance.
The RFID system comprises three main components. They are the tag, the reader, and finally, the software. The tags are attached to the things that are to be tracked and they consist of a microchip and an antenna. Readers are devices that emit radio waves and communicate chemically with the tags, requiring data retrieval. The software integrates the data into a database that will provide real-time insights and analytics. This entire frame setup allows very high automation in tracking to minimize errors in manual tracking while improving the efficiency of operations.”
Applications of RFID in Healthcare
There are various applications of RFID technology-a new dimension to healthcare environments:
Medical Equipment Tracking: Every piece of equipment connected to the patient, such as IV pumps, ventilators, and defibrillators, has an attached RFID tag for tracking and monitoring their respective locations, as well as their usage. For example, in critical surgery, knowing the exact location of a specific surgical instrument can save precious minutes.
Medical equipment tracking also serves theft or loss prevention purposes. Because most hospitals do not have good tracking for expensive medical devices, they disappear into thin air. RFID tags can be programmed to notify security if an item is taken off its vendor areas, thus stopping it from being taken out without authorizing those certain access points.
Inventory control is of tremendous importance during pandemics or outbreaks when the demand for particular supplies might spike suddenly. The RFID technology enables the healthcare establishment to respond quickly by providing up-to-date information on the stock available at a given time and therefore expedite the procurement of supplies when needed.
Patient verification is essential in emergencies, where identification made efficiently and accurately can be a matter of life and death. RFID wristbands harbor valuable patient information such as allergies or some medical condition indexes for swift access by caregivers.
Compliance and Maintenance: RFID maintains tracking of sterilization records, maintenance schedules, and calibration history of medical devices for regulation compliance, especially important for surgical instruments requiring precise calibration and sterilization before use. RFID assures that these processes are documented and up-to-date to minimize either the risk of infection or malfunctioning of the device.
Cryogenic Sample Management: Monitoring biological samples stored in cryogenic conditions using RFID ensures maintaining the most suitable conditions for storage.
When it comes to research and its primary area of application in making medical discoveries, cryogenic sample management is indispensable. Such samples should maintain their integrity by RFID tracking of their storage conditions and ensure that sufficient traceability is provided to prevent loss or mistreatment.
Here are some advantages of RFID Asset Tracking in Healthcare
1. Operational Efficiency
RFID automates various manual tasks: inventory checks, equipment searches, and several others. Staff wastes no time searching for devices or supplies and can locate one in seconds after RFID adoption. This allows for time to concentrate on patient care and reduces costs in labor.
2. Cost Reduction
By providing real-time inventory data, RFID helps avoid overstocking as well as stockouts. This further leads to adequate financial management.
By automating inventory management and equipment tracking, healthcare organizations can save labor costs, allowing them to focus on higher-value activities such as patient care and research. check out latest blog post on What are the main benefits of using RFID asset tracking over traditional methods
3. Improved Patient Safety
RFID greatly reduces errors in identifying patients coming in for treatment and surgery. They also ensure proper maintenance and sterilization of medical devices before timely use. In doing so, they greatly reduce the incidence of infection or malfunction.
4. Real-Time Data Insights
RFID systems collect real-time data on asset usage patterns, inventory levels, and patient movements. This insight helps optimize workflow, keeps resource allocation smooth, and reinforces decisions in this regard. For example, RFID data reveals bottlenecks in patient care processes and allows enhancements on those fronts from the facility.
The real-time insights also enable predictive analytics. Anticipation of future needs and adaptation of procurement strategies by analyzing usage patterns and inventory levels ensure that healthcare facilities can manage supply chains effectively while keeping stockouts at bay.
5. Regulatory Compliance
RFID helps healthcare organizations meet stringent regulations without manual supervision by automatically tracking sterilization records and maintenance schedules. This alleviates the administrative burden and ensures that in case of audits, all required documentation is readily available.
Regulatory compliance is vital for maintaining accreditation and avoiding fines. RFID automation of compliance checks means hospitals can consistently make sure they meet all the regulatory standards. Ultimately, this saves costs incurred in non-compliance and equally enhances the good name of healthcare establishments as being stakeholders in quality care.
Challenges in Implementing RFID
Despite its many benefits, the implementation of RFID in healthcare poses challenges:
High Initial Costs: The upfront investment of the RFID system would be considerably high. It involves the cost for tags, readers, software integration, and training staff. Therefore, although RFID offers cost savings in the long run, the initial investment becomes a hindrance for small healthcare institutions with less budget.
Privacy Concerns: Tracking patients’ movements could be a matter of privacy if the security of the data is not ensured to any reasonable extent. Healthcare facilities must secure RFID data involving patient tracking through encryption and secured storage.
Technical Barriers: Integrating RFID systems into the existing hospital infrastructure can prove less than straightforward due to incompatibility issues or a nonexistent knowledge base among the technicians.
Technical constraints can come into play during the integration of RFID into the existing hospital infrastructure mainly because of compatibility issues or a lack of technical know-how. Thus, healthcare needs to invest in IT support to accomplish an uninterrupted integration process.
Resistance to Change: Setting up new technologies is always shunned by non-familiarity, increased workload apprehension, etc., during the transition phases. Training and communication are potent means to eradicate resistance.
Moreover, by demonstrating the advantages of RFID and encouraging staff participation within decision-making, healthcare organizations can further legitimize the technology and move forward to successful implementation.
Future of RFID in Healthcare
With the ability to kill two birds with one stone, its efficiency will solve operational challenges, and IoTs will increase their fortitude even further with predictive analytics for the maintenance of their equipment or patient care optimization.
These include the enhancement of tag technology and more miniaturization of tags with increased durability against the onslaught of hostile environments. Moreover, improvement in data analytics will enable healthcare establishments to harvest more insight from the RFID data, which is going to be another important aspect of optimizing their operation and patient care.
Conclusion
Asset tracking through RFID is bringing a major change in healthcare operations by increasing workflow efficiencies, improving patient care, lowering costs, and enhancing safety measures. Despite challenges such as excessively high implementation costs and privacy concerns, the benefits greatly outweigh the cons. With further technological advancement, contact us as RFID will continue playing an important role in shaping efficient and patient-oriented healthcare systems.
Organizations in the healthcare sector intending to deploy implementations of RFID must strategize such plans that tackle barriers while outlining how to maximize operational excellence. Armed with RFID technology, healthcare facilities would be ready for success within the dynamic and changing healthcare environment.